The University of the Cordilleras (UC), through its Campus Management Office (CMO), reaffirms its strong commitment to sustainability, operational efficiency, and environmental responsibility as reflected in the 2024 Annual Report. Guided by global sustainability principles, UC continues to develop resilient, energy-efficient, and environmentally responsible infrastructure advancing its alignment with the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
Sustainable Infrastructure Development
UC spearheaded several infrastructure projects promoting preventive maintenance, energy efficiency, and climate resilience. These include waterproofing and structural protection works that extend the life of building components and prevent material waste, the renovation of the main canteen with energy-efficient lighting and improved ventilation, and the preventive maintenance of electrical and mechanical systems to minimize energy waste and operational disruptions.
Regular façade cleaning, ventilation system upgrades, and the installation of energy-efficient glass partitions further promote energy conservation and healthier indoor environments. Water system improvements, such as replacing old G.I. tanks with stainless steel units, enhance water storage efficiency, reducing leak-related losses and supporting responsible water resource management. Moreover, the rehabilitation of the storm drain canal strengthens the University’s climate resilience by improving stormwater flow and mitigating flood risks.
UC continues to uphold its commitment to operational efficiency and facility optimization through comprehensive in-house and preventive maintenance programs. These efforts encompass janitorial services that maintain campus cleanliness and hygiene, carpentry works for the upkeep of wooden structures and furniture, painting services that preserve aesthetic appeal and surface protection, and electrical works that ensure reliable power systems through routine inspections and upgrades. In addition, preventive maintenance for mechanical and electrical systems is implemented regularly to sustain equipment efficiency and extend service life. This proactive approach not only enhances the functionality and safety of university facilities but also minimizes energy waste, supports sustainable resource management, and reinforces UC’s dedication to a clean, resilient, and environmentally responsible learning environment.
Sustainable Construction Initiatives
The Campo Libertad Development Project, one of UC’s flagship sustainability initiatives, integrates eco-efficient features such as rooftop solar panels for renewable energy, rainwater harvesting systems for non-potable water applications, and a sewage treatment plant (STP) for responsible wastewater management. These efforts exemplify UC’s dedication to the principles of SDG 6 (Clean Water and Sanitation), SDG 7 (Affordable and Clean Energy), and SDG 13 (Climate Action) by reducing environmental impact and promoting the reuse of natural resources. The project is currently ongoing, with the latest milestone marking the completion of concrete pouring for beams and the 4th-floor slab.
Plans are also underway to install solar panels across the Main Campus. This initiative will support UC’s goal of energy independence and reduce reliance on non-renewable electricity, directly contributing to the reduction of carbon emissions and operational costs while supporting green campus certification efforts.
Water Quality and Usage Monitoring
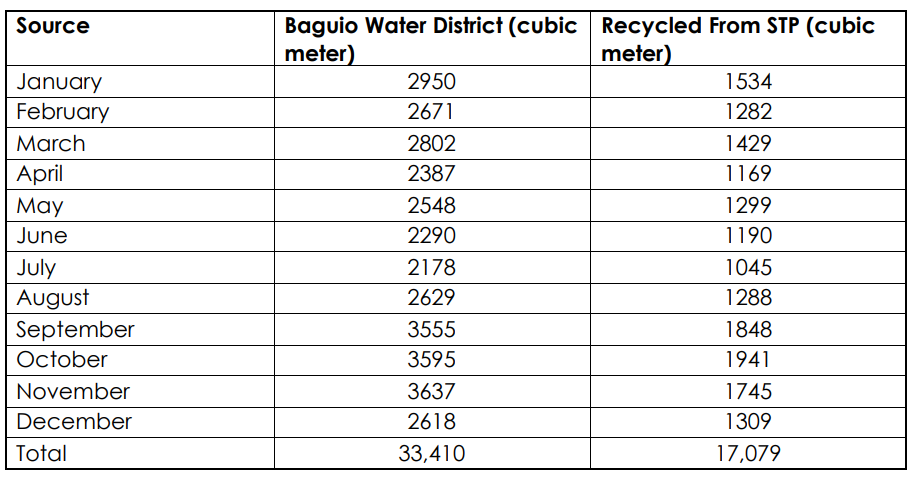
The University of the Cordilleras (UC) recorded a total 2024 water consumption of 33,410 cubic meters from its main supply, the Baguio Water District, of which 17,079 cubic meters were recycled through the university’s treatment system. This remarkably low water footprint reflects the university’s effective conservation measures. Of this total, 17,079 cubic meters came from recycled water processed through UC’s Sewage Treatment Plant (STP), demonstrating its strong commitment to water reuse and sustainable resource management. These efforts strengthen UC’s pursuit of SDG 6: Clean Water and Sanitation.
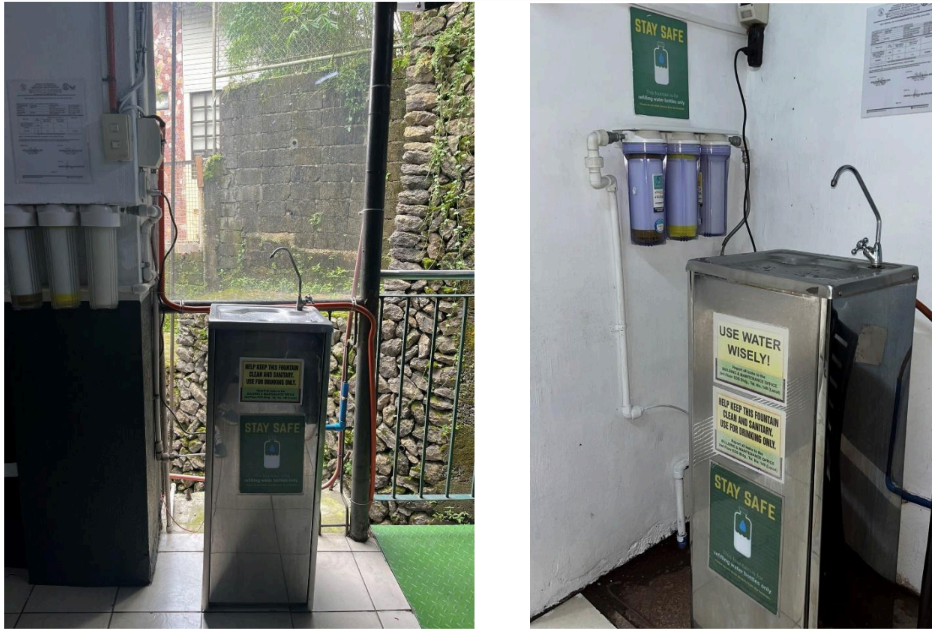

A total of nine (9) drinking fountains are strategically installed across the UC campuses, two units at the Legarda Campus and seven at the Main Campus providing accessible, clean and free drinking water for students and employees. To ensure the safety and potability of drinking water for students and employees, microbiological water analyses are conducted quarterly. These regular tests help verify that the water meets the required health and safety standards. In addition to water quality monitoring, the university implements a preventive maintenance program for all drinking fountains. This includes routine cleaning, inspection, and timely repair of components to maintain optimal functionality and sanitation. Through these continuous efforts, UC upholds its commitment to providing a safe, healthy, and sustainable learning environment while promoting responsible water consumption within the university community.
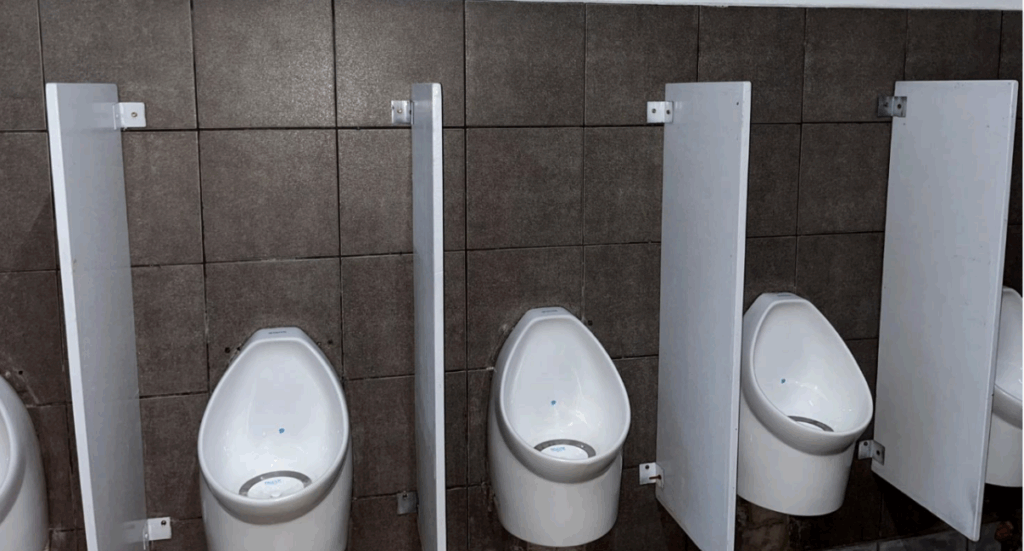
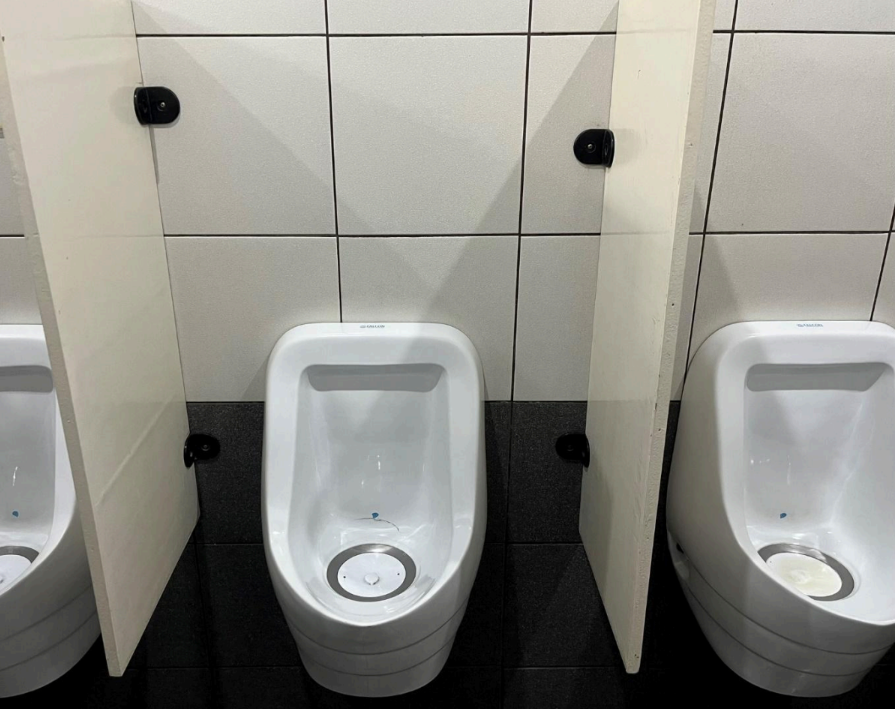


UC has implemented effective and data-driven strategies to significantly reduce water consumption across its campuses. One of the key efforts under this program is the replacement of traditional urinals with waterless urinals, a move that significantly reduces water consumption and lowers the university’s operational costs. Based on 2024 data, UC recorded a total of 98 urinals installed across its campuses, of which 53 units or 54.08% are water-efficient models. This means that more than half of the university’s urinals are now
waterless, contributing to substantial water savings each day. The transition to these eco-friendly fixtures not only reduces the volume of water used for sanitation but also minimizes the environmental impact of daily operations.
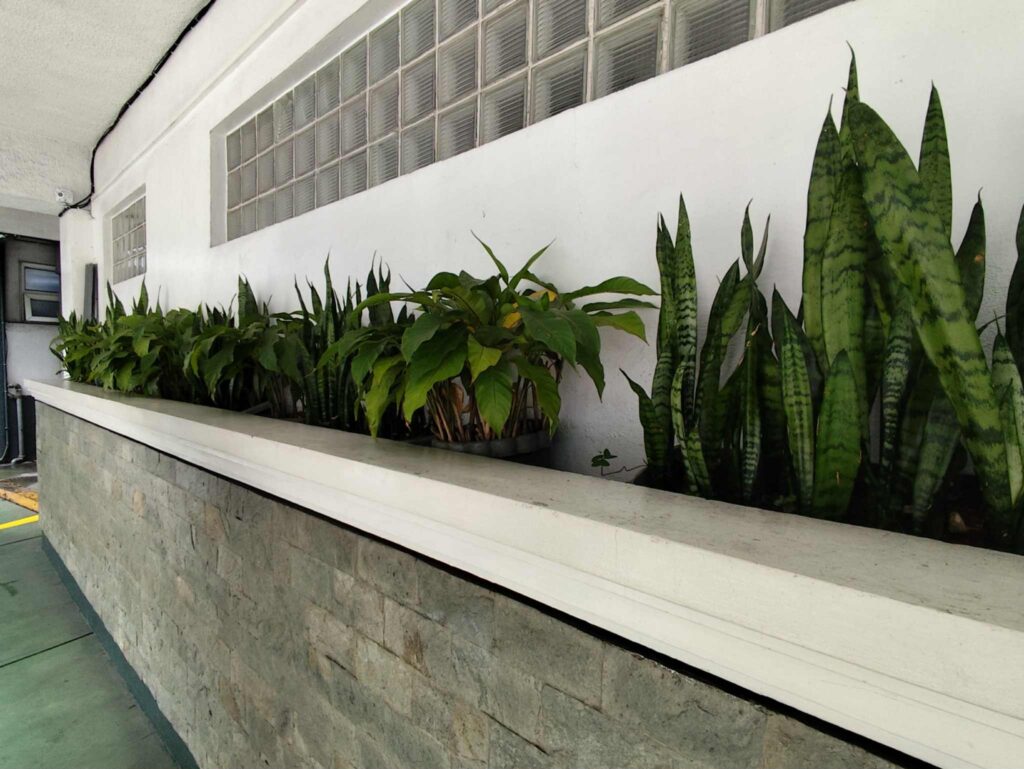
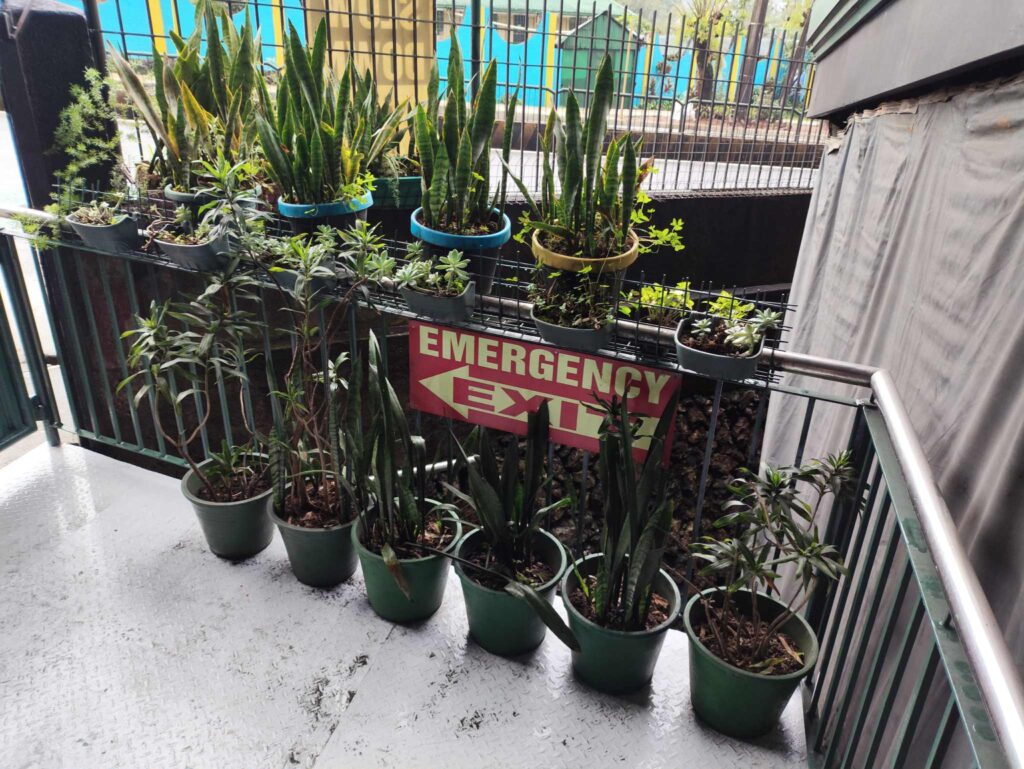


UC also integrates water-conscious planting in its campus landscaping as part of its broader sustainability and environmental management initiatives. This approach aims to reduce water consumption, maintain ecological balance, and enhance the resilience of green spaces during dry periods.
This initiative demonstrates the university’s proactive approach to water conservation through technological upgrades and sustainable facility management. By steadily increasing the number of water-efficient fixtures, UC shows measurable progress toward reducing its overall water footprint. Moreover, the adoption of waterless systems aligns with Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) 6 – Clean Water and Sanitation and SDG 12 – Responsible Consumption and Production, as it encourages efficient water use and supports long-term
sustainability practices.
Wastewater Treatment and Water Reuse
The University operates a Sewage Treatment Plant (STP) with a capacity of 1,200 cubic meters per day. The system treats wastewater from toilets, sinks, and other facilities, ensuring compliance with DENR Administrative Order No. 2016-08 and the Philippine Clean Water Act (RA 9275). To enhance treatment efficiency, an Advanced Reverse Osmosis (RO) system was installed as the final treatment stage, enabling the safe reuse of treated wastewater for toilet flushing and landscape irrigation. This process significantly reduces the University’s potable water demand.
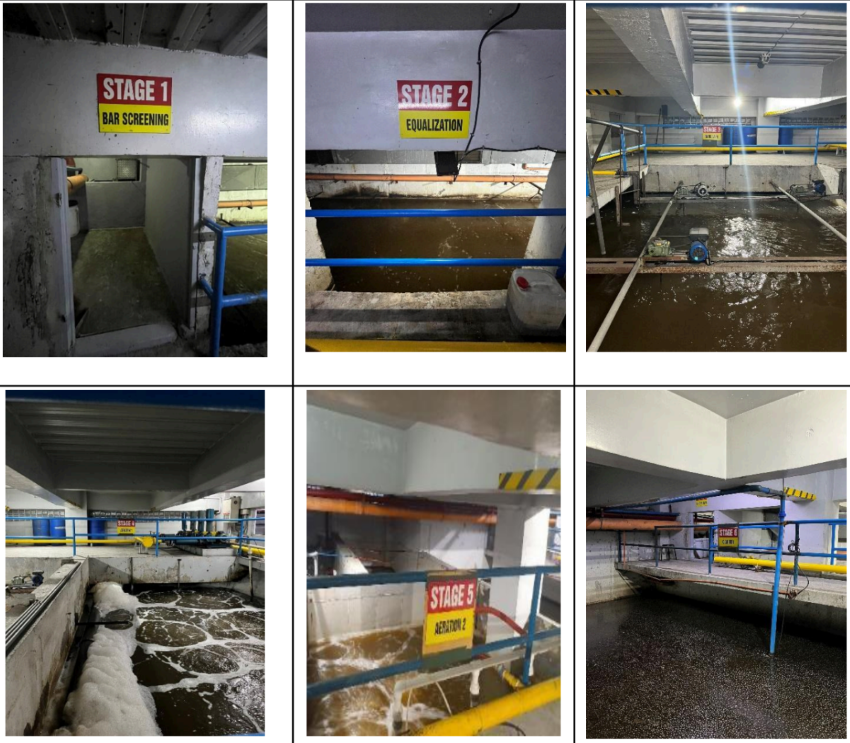

Complementing this, is the activation of a rainwater harvesting system, which collects and filters rainwater from building rooftops for integration with recycled wastewater, further supporting water reuse and resilience against water supply disruptions.

The university ensures safe water management by preventing pollution, storing potable water properly, and treating wastewater effectively. Drinking water is kept in dedicated tanks separate from non-potable or recycled water to maintain quality. Wastewater from toilets, sinks, and lavatories is treated in the sewage treatment facility according to national effluent standards and monitored quarterly to prevent contamination of surrounding water systems. Additionally, rainwater is harvested, filtered, and stored for non-potable uses such as toilet flushing and landscaping, reducing reliance on potable supply. These integrated measures protect water quality and supports sustainable water extraction by maximizing the use of alternative water sources such as rainwater and treated wastewater.
Waste Management and Recycling
UC’s solid waste management program supports SDG 12 (Responsible Consumption and Production) through systematic waste segregation, composting, and recycling practices. In 2024, the university produced 14.438 tons of organic waste, including food scraps, leaves, and biodegradable materials, which were processed through vermicomposting to create organic fertilizer for campus landscaping. Leftover food from canteens was reused as animal feed, reducing landfill contributions.

For inorganic waste, a total of 24.791 tons were generated, including 1.733 tons of metals, 5.609 tons of paper, 0.757 tons of monoblocks, and 0.114 tons of plastic bottles. These materials were sorted and sold to local junk shops through the Logistics Management Office, contributing to the circular economy and promoting recycling efforts.
In terms of hazardous waste management, UC handled 2.3062 tons of toxic materials such as waste electrical and electronic equipment (WEEE), laboratory chemicals, pathological wastes, and toxic chemical containers. All were properly treated and disposed of through accredited Environmental Management Bureau (EMB) waste treaters, ensuring full regulatory compliance.
Energy Management and Climate Action
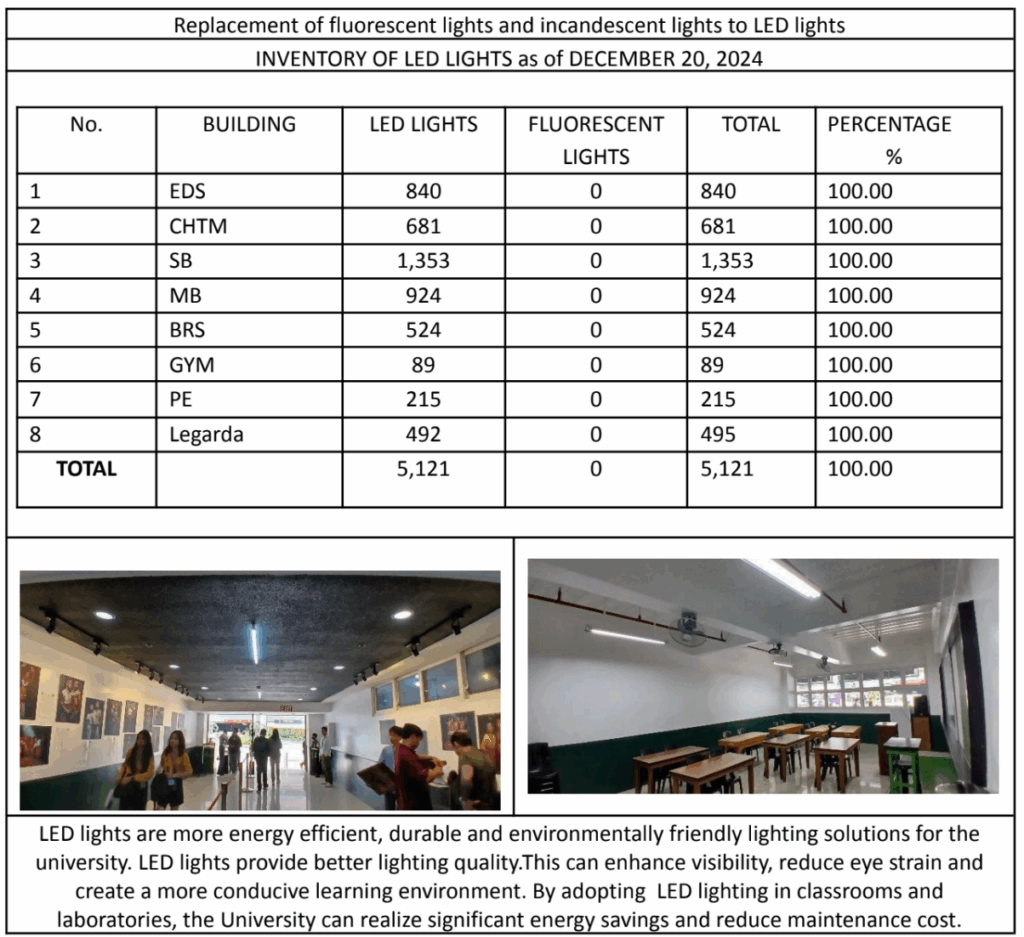
The University consumed a total of 938,689 kWh of electricity in 2024. Energy is primarily used for lighting, mechanical systems, laboratory equipment, and digital learning facilities. With all campus buildings now fully upgraded to LED lighting systems (5,268 units), UC achieved a 100% transition from fluorescent and incandescent bulbs, reducing electricity consumption by 50–70% and minimizing maintenance costs.
The University’s energy initiatives directly contribute to SDG 7 (Affordable and Clean Energy) and SDG 13 (Climate Action) through reduced greenhouse gas emissions and energy-efficient practices. Moreover, UC plans to conduct a comprehensive energy audit in 2026 to identify new opportunities for renewable integration and carbon footprint reduction.
In 2024, the University recorded a total energy consumption of 3,426 gigajoules (GJ) across its facilities, covering a total floor area of 67,706 square meters. This translates to an average energy usage of approximately 20 GJ per square meter, reflecting the institution’s ongoing efforts to optimize energy efficiency within its academic, administrative, and laboratory spaces. The data underscores the University’s commitment to monitoring and managing its energy footprint as part of its broader sustainability initiatives.
In line with these efforts, UC declares a 100 % Renewable Energy Pledge, committing to source all campus electricity from renewable energy through a phased approach. Annual reports will track progress, including shares of renewable energy and energy-efficiency upgrades.
Through integrated programs in wastewater treatment, rainwater harvesting, waste management, and energy conservation, the University of the Cordilleras demonstrates its steadfast commitment to sustainability. These initiatives embody the institution’s proactive response to environmental challenges, reducing resource consumption, enhancing operational efficiency, and nurturing a campus culture rooted in environmental stewardship.
In alignment with the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals, UC continues to build a greener, more resilient, and sustainable future, empowering its community to lead change through responsible and conscious action.